For years, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) has been the go-to model for digitizing business operations. From managing customer relationships to tracking payroll, SaaS helped companies move faster and smarter in the cloud. However, something more powerful is beginning to take shape that not only supports workflows but also takes action. Welcome to the era of Vertical AI Agents.
These agents don’t just live inside dashboards waiting for instructions. They’re industry-specific AI professionals who can understand, decide, and execute. Unlike broad AI tools like ChatGPT or Copilot, Vertical AI is designed to master the nuances of a single domain, such as healthcare, law, finance, real estate, or logistics, and operate almost like a domain expert.

What Is Vertical AI?
Let’s break it down.
Vertical AI refers to AI solutions designed for a specific industry. While horizontal or general-purpose AI serves a wide range of tasks, vertical AI, also known as AI vertical, focuses intensely on a particular niche. It’s trained on industry-specific data, language, and regulations, giving it the kind of expertise you’d expect from a seasoned professional in that field.
If you’re wondering what vertical AI is, here’s a simple answer: It’s artificial intelligence that understands your business inside and out.
For example:
- Healthcare: An AI that understands EMRs, insurance codes, and patient scheduling
- Legal: An AI that drafts legal contracts, does research, and checks compliance.
- Finance: An AI that underwrites loans, evaluates risks, and flags fraud.
These aren’t just digital tools; they’re becoming digital experts, and often, they take form as Vertical AI Agents.

So, What Are Vertical AI Agents?
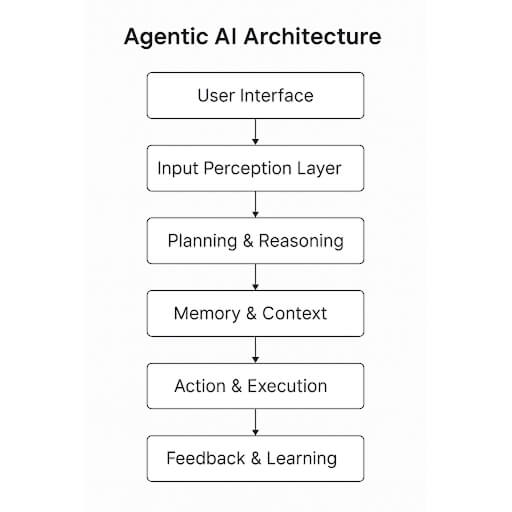
Vertical AI Agents are like specialized coworkers who live inside your software systems. They’re built to perform high-stakes tasks in a specific domain, without needing you to hold their hand every step of the way.
What can they do?
- Read and understand complex documents, such as contracts or claims.
- Make decisions, like approving a mortgage or flagging a suspicious transaction.
- Chat with users or systems to keep processes moving.g
- Learn and adapt to your industry’s evolving rules and workflows.
Real-world examples of how they work:
- Insurance: An agent handles claims, spotting red flags, verifying coverage, and updating clients automatically.
- Real Estate: AI manages listings, schedules site visits, handles paperwork, and even analyzes local market data.
- Healthcare: An agent processes pre-authorizations, summarizes patient visits, and helps doctors stay focused on care, not admin.
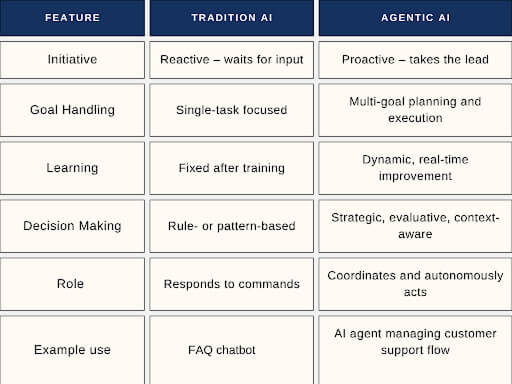
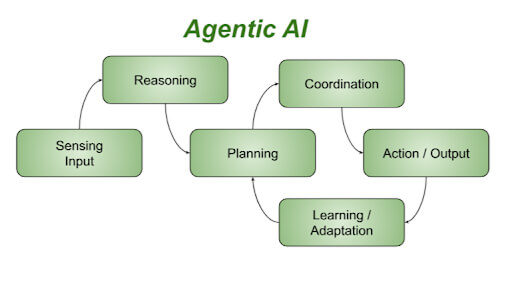
The key difference? These agents aren’t rule-based bots. They’re proactive, intelligent, and trained to operate with confidence inside specific AI verticals.
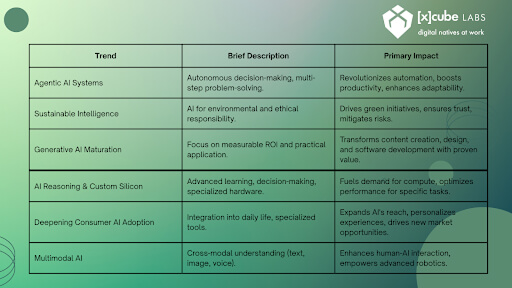
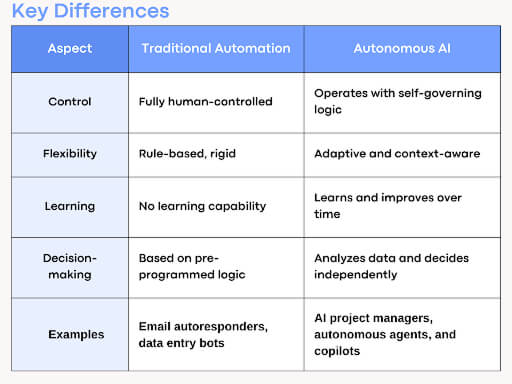
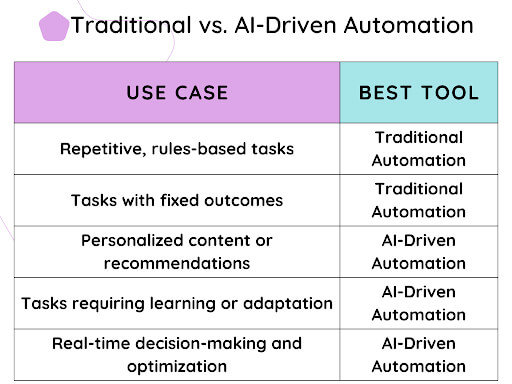
Vertical AI vs Horizontal AI: What’s the Big Deal?
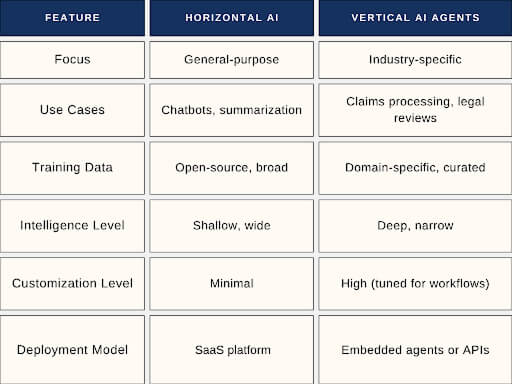
This comparison illustrates why vertical AI agent technology is gaining ground over traditional AI platforms that spread thin across too many use cases.
Why Vertical AI Agents Are the Future of Automation
The buzz around vertical AI agents isn’t just hype; real-world results drive it. More and more companies are turning to agents that aren’t just smart, they’re tailor-made for their business.
Here’s why they’re taking off:
- Laser-focused: Trained on the exact documents, tasks, and language of your industry
- Truly autonomous: Doesn’t need constant instructions
- Safe and compliant: Built with regulations like HIPAA or SOC2 in mind
- Plug-and-play ready: Integrates with the tools your team already uses, CRMs, ERPs, or EHRs
This isn’t about giving your team a new dashboard. It’s about giving them a digital partner who gets the job done quietly, efficiently, and 24/7.
The big benefits:
- Lower costs: Automates repetitive and manual work
- Faster decisions: No more waiting on people for every approval
- More accuracy: Learns from real-world feedback and improves over time
- Scalability: Grows with your business, with extra hiring needed
According to McKinsey, businesses that use vertical AI report efficiency gains of 25–50%. One study found that over two-thirds of enterprises experienced improved customer service within the first year of implementation.

Real-World Examples: How Industries Are Already Using Vertical AI
Healthcare: Hippocratic AI
This agent handles tasks such as post-visit follow-ups, care navigation, and insurance-related questions, as well as diagnosis requirements, all with the goal of smooth coordination. In 2023 alone, vertical AI healthcare startups raised over $2.3 billion in funding.
Legal: Harvey AI
Harvey assists lawyers in drafting documents, conducting legal research, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. It’s already in use by 15+ global law firms, demonstrating the rapid adoption of vertical AI agents in regulated industries.
Real Estate: Perchwell
It supports agents and brokers by offering property insights, automating listings, and personalizing recommendations for buyers and sellers.
Finance: Underwrite.ai
Goes beyond credit scores to evaluate a borrower’s actual risk, reducing defaults by up to 20% by tapping into alternative data, according to JP Morgan.
What do they all have in common? Context. Precision. Confidence.
These tools don’t need to “learn your business”; they already speak its language, and that’s the core strength of a vertical AI agent.
A Growing Market: The Vertical AI Market Map
The vertical AI market map is growing fast, and it’s filled with opportunities. Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, there’s increasing pressure to move beyond generic AI and invest in verticalized solutions.
Consider these stats:
- $3.5B+ in VC funding for vertical AI startups in 2023.
- Gartner says 30% of enterprise AI deployments will be vertical-specific by 2026.
- Companies utilizing vertical AI agents have achieved productivity gains of up to 40%.
- 76% of enterprises say vertical AI is “critical” for digital transformation.
The AI vertical shift is no longer just a trend; it has become a strategic necessity.
Challenges Still Exist, but They’re Worth Tackling
Like any tech revolution, the shift toward vertical AI agents comes with its own set of challenges.
The biggest hurdles:
- Obtaining high-quality data: Agents require accurate, labeled, and relevant domain data to train effectively.
- Regulatory compliance is critical in finance, legal, and healthcare, where the cost of mistakes is high.
- Legacy systems: Many businesses still operate on outdated technology, requiring agents to integrate with existing systems.
- User trust: People need to trust the AI to do its job right and support, not replace, their work.
Gartner notes that 41% of failed AI projects fail because they didn’t align well with industry-specific needs. The lesson? Specialization matters.
The Future Is Human + AI: Vertical Agents as Digital Teammates.
We’re moving into a world where vertical AI agents will become part of the team, handling the routine so that humans can focus on strategy, relationships, and creativity.
What’s coming:
- Agents embedded in every business tool
- LLMs are fine-tuned for industry regulations.
- Hybrid workforces, where AI and humans share responsibilities
They’re not taking jobs, they’re changing how jobs get done.

Final Thoughts
The SaaS era helped digitize work. Vertical AI agents are now doing the work.
If your company is wondering how to stay competitive in the AI era, here’s a tip: don’t just look for generic AI tools. Find or build a vertical AI agent that understands your business as well as your top performer, and never needs a break.
This is the new frontier beyond SaaSand; it’s already in motion.
FAQs
1. What is Vertical AI?
It’s AI designed for specific industries, such as healthcare or finance, with deep domain expertise.
2. How’s it different from general-purpose AI tools?
Vertical AI agents are specifically tuned to the exact workflows and terminology of a particular industry. They outperform general AI in specialized tasks.
3. Are companies using this already?
Yes. From real estate to legal to insurance, many firms are already using vertical AI agents to automate and accelerate work.
4. What does the future look like?
By 2026, most enterprise AI tools will be verticalized, bringing more intelligent automation, better service, and deeper integration into daily business through the vertical AI market map.
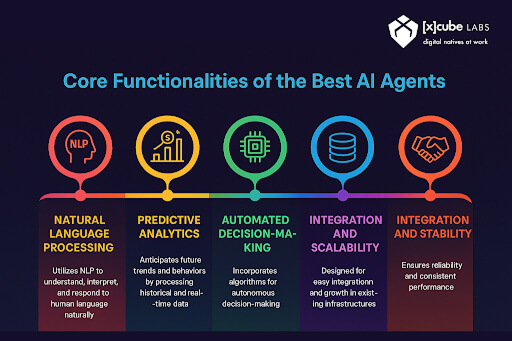
How Can [x]cube LABS Help?
At [x]cube LABS, we craft intelligent AI agents that seamlessly integrate with your systems, enhancing efficiency and innovation:
- Intelligent Virtual Assistants: Deploy AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants for 24/7 personalized customer support, streamlining service and reducing call center volume.
- RPA Agents for Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like invoicing and compliance checks, minimizing errors and boosting operational efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics & Decision-Making Agents: Utilize machine learning to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and provide real-time strategic insights.
- Supply Chain & Logistics Multi-Agent Systems: Enhance supply chain efficiency by leveraging autonomous agents that manage inventory and dynamically adapt logistics operations.
- Autonomous Cybersecurity Agents: Enhance security by autonomously detecting anomalies, responding to threats, and enforcing policies in real-time.
- Generative AI & Content Creation Agents: Accelerate content production with AI-generated descriptions, visuals, and code, ensuring brand consistency and scalability.
Integrate our Agentic AI solutions to automate tasks, derive actionable insights, and deliver superior customer experiences effortlessly within your existing workflows.
For more information and to schedule a FREE demo, check out all our ready-to-deploy agents here.
 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783