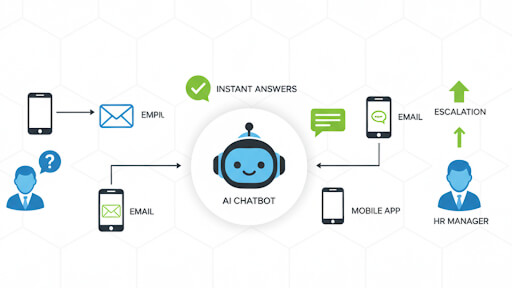
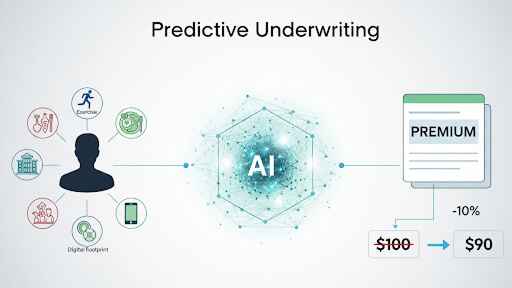
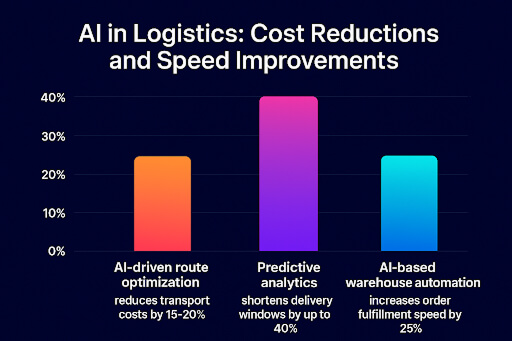
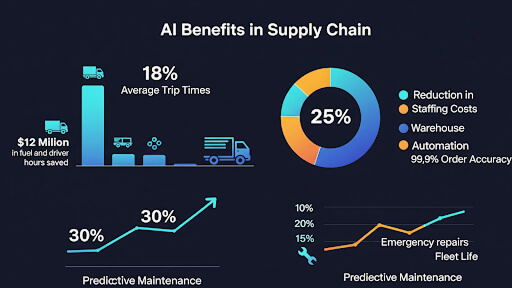
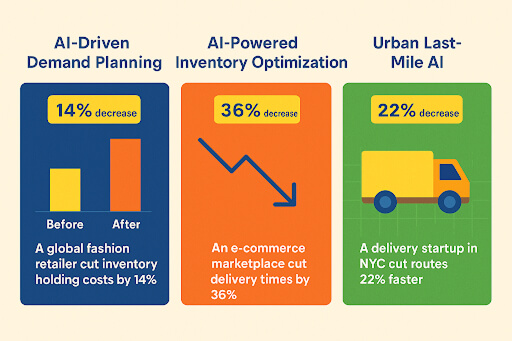
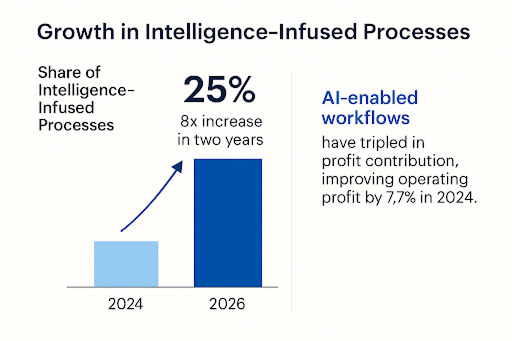
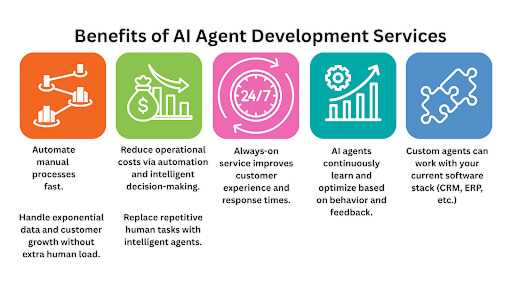
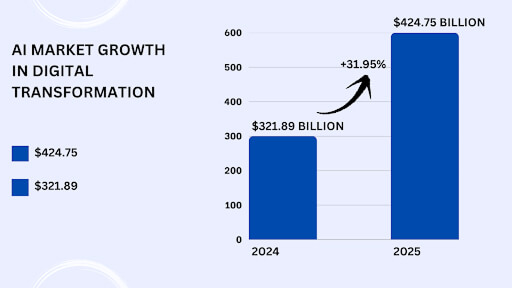
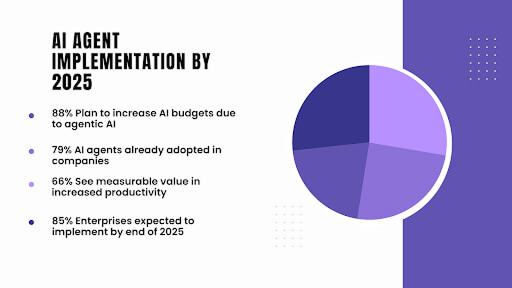
The future of customer interaction isn’t typed, it’s spoken. Voice AI agents represent the next giant leap in conversational artificial intelligence, moving past simple commands to offer truly human-like, autonomous service.
This technology is rapidly transitioning from a smart home novelty to a critical business tool, dramatically reshaping operations.
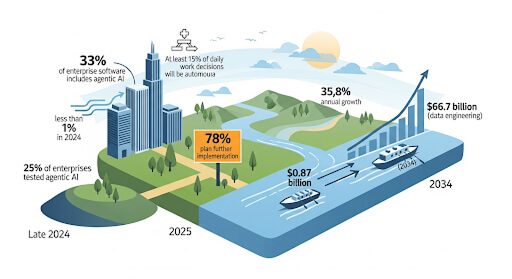
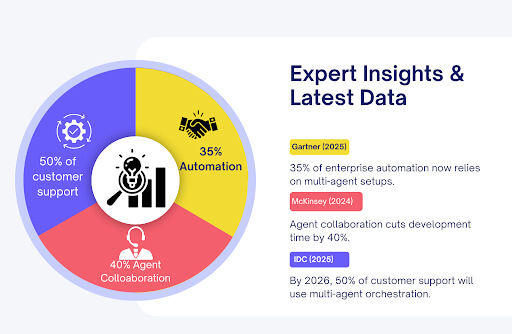
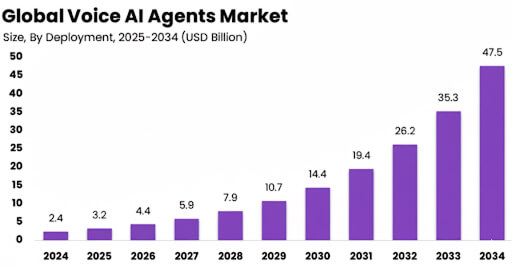
In fact, the global Voice AI agents market is projected to skyrocket from $2.4 billion in 2024 to nearly $47.5 billion by 2034, growing at an astonishing CAGR of 34.8%.
This explosive growth is driven by the desire for efficiency and a better customer experience.
Nearly 89% of customers now favor brands that provide support through Voice AI technologies.
These intelligent agents are not just answering questions; they are revolutionizing the way businesses interact, scale, and deliver value.
What are Voice AI Agents?
A Voice AI Agent is a type of artificial intelligence that utilizes advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP), Speech-to-Text (STT), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) technologies to facilitate real-time conversations.
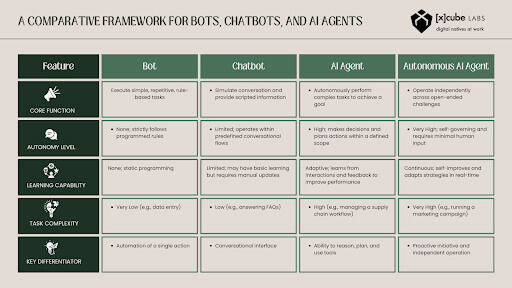
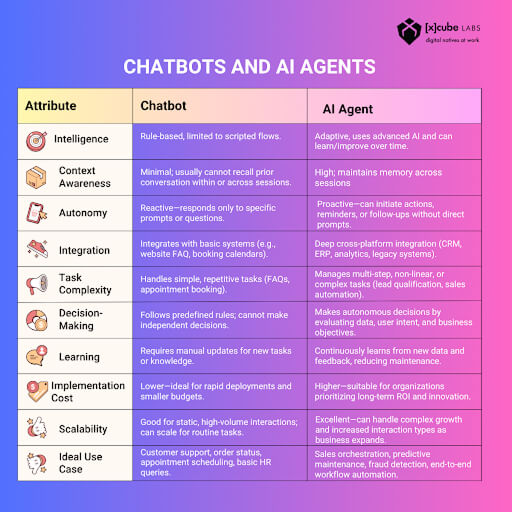
Modern AI agents are characterized by their agentic capability, which distinguishes them from traditional bots. These “agentic” systems have:
- Autonomy: They can operate and make decisions independently without constant human oversight.
- Reasoning and Planning: They break down complex requests into smaller steps and plan actions before executing them.
- Memory and State Tracking: They maintain context throughout an extended conversation (short-term memory) and can refer to past interactions or data (long-term memory) to personalize future service.
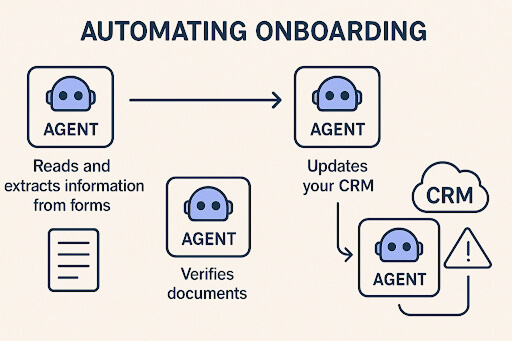
- Tool Use: They leverage external resources, such as internal enterprise databases, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and specialized Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to process transactions and fetch real-time information.

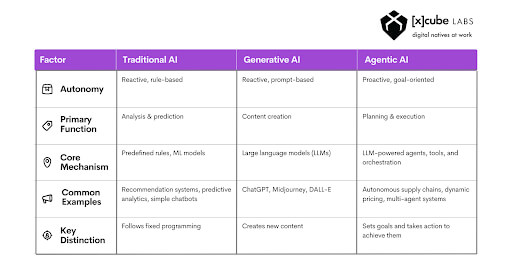
These abilities make Voice AI Agents very different from traditional systems.
A conventional IVR reacts and follows a fixed decision tree. It mainly routes calls or gives pre-recorded information.
A Voice AI Agent is proactive. It utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate dynamic responses, offer personalized solutions, and quickly troubleshoot, making conversations feel like speaking to a highly knowledgeable assistant.
Why are Voice AI agents Important?
The importance of Voice AI Agents is rooted in three critical business drivers: meeting escalating customer expectations, achieving operational scalability that is impossible with human-only teams, and the need for data-driven, personalized experiences.
1. The Customer Demand for Immediacy
Customers now expect instant, 24/7 service. Relying on human agents alone makes achieving this service level prohibitively expensive. AI agents eliminate hold times, offering instant concurrency and the ability to handle thousands of calls simultaneously, regardless of time or day. The trade-off that businesses once made, sacrificing speed for cost savings, is no longer necessary.
2. Unprecedented Operational Scalability
Traditional call centers struggle with seasonal peaks, unexpected high-volume events, and agent attrition. Voice AI Agents are inherently scalable, cloud-native resources. They can instantly absorb call volume spikes without the need for additional hiring, training, or infrastructure investment. This elasticity is crucial for businesses with unpredictable or rapidly growing contact volumes.
3. Consistency and Compliance
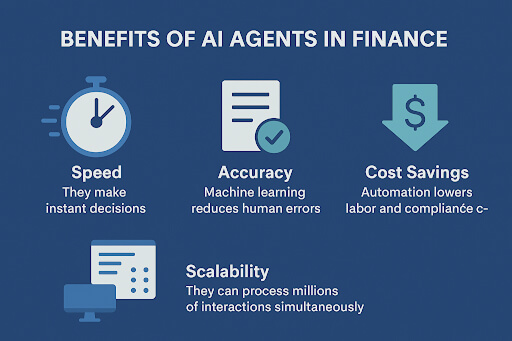
Human agents, however well-trained, are subject to fatigue, variation in quality, and human error. AI agents deliver a perfectly consistent, on-brand response every single time, ensuring adherence to regulatory compliance and company policy. Furthermore, every interaction is transcribed, analyzed, and logged, creating a comprehensive audit trail essential for highly regulated industries such as finance and healthcare.
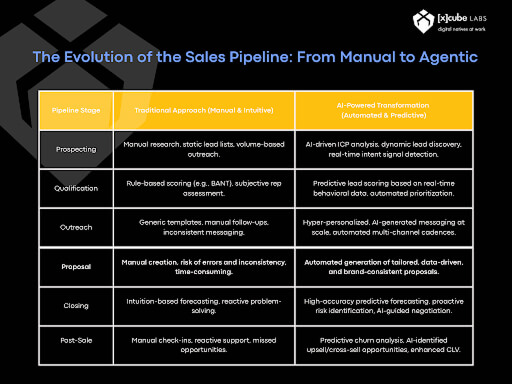
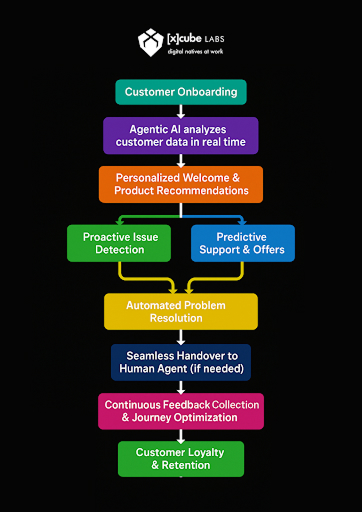
How do Voice AI Agents Work
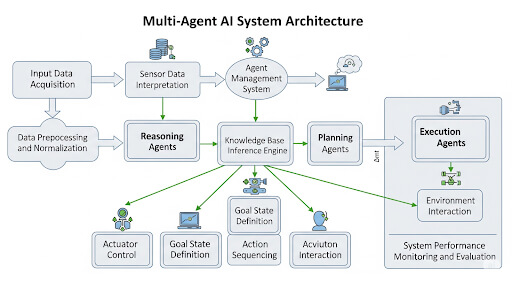
A successful Voice AI Agent utilizes a tightly integrated, multi-layered architecture that processes the complete conversational loop in sub-second timeframes. Understanding how these system components interact is essential for achieving a natural, human-like pace.
The Conversational Pipeline
The process can be broken down into four core, real-time steps:
1. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Noise Handling
The conversation begins when the user’s spoken words are captured and converted into text. At this initial stage, modern ASR models filter background noise, handle interruptions (enabling full-duplex conversation), and accurately interpret diverse accents and speaking styles.
2. Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Intent Mapping
Next, the transcribed text is analyzed for meaning. The NLU engine identifies the user’s primary intent (e.g., cancel order, check balance), extracts entities (e.g., order numbers, dates), and detects sentiment. This crucial step ensures the agent knows not just what was said, but why it was said and the user’s emotional state.
3. Reasoning and Agentic RAG
This step serves as the “brain” of the agent, where the Agentic RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipeline operates by applying reasoning to retrieved, relevant information. It combines the retrieval of necessary external knowledge with the language model’s ability to generate accurate, contextually relevant responses, ensuring the agent can precisely answer complex, knowledge-based queries.
- Planning: If the request is complex (e.g., “I need to upgrade my plan and know the new monthly cost”), the agent breaks it into steps: 1) Identify current plan, 2) Retrieve upgrade options, 3) Calculate new cost.
- Retrieval: The agent then uses its tool-use capability to dynamically fetch contextually relevant, real-time data from internal databases, CRM systems, and knowledge articles. This grounding information is used to “augment” the Large Language Model.
- Generation: The LLM synthesizes a clear, context-aware response using only the retrieved facts, minimizing hallucination.
4. Text-to-Speech (TTS) and Latency Management
The final, synthesized text response is converted back into high-fidelity, natural-sounding speech. Critical to the perception of a natural conversation is ultra-low latency. Top-tier systems aim for a round-trip response time (from the moment the user stops speaking to the moment the agent begins replying) of less than 1200 milliseconds.

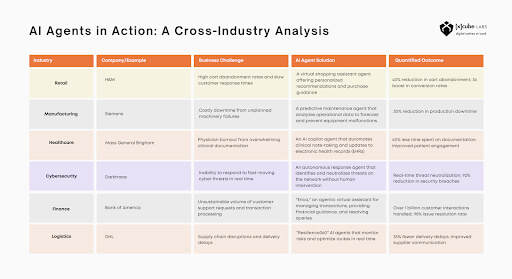
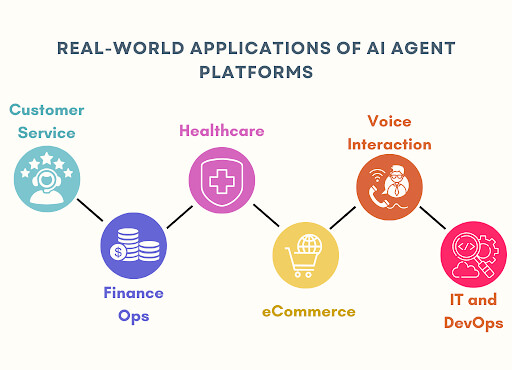
Use Case of Voice AI Agents
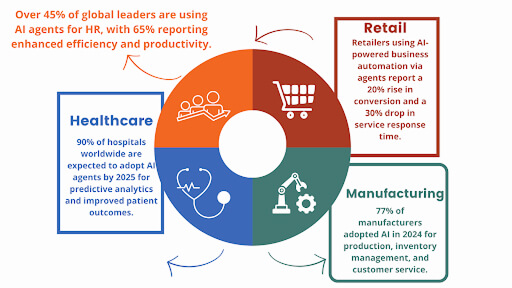
The versatility of the best AI voice agents enables them to drive significant value across nearly every industry, particularly those with high call volumes and complex data requirements.
Financial Services and Banking
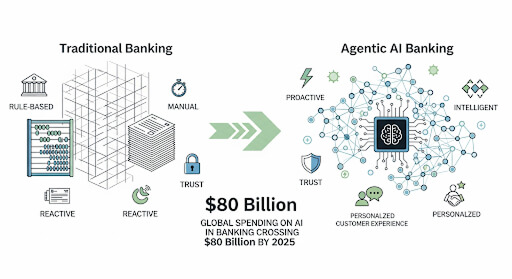
In this highly regulated sector, AI voice agents for customer service excel at secure, compliant transactions. The BFSI sector led with a 32.9% share in 2024, showcasing Voice AI’s role in transforming customer experience.
- Account Management: Securely checking account balances, recent transactions, or payment due dates using voice biometrics for authentication.
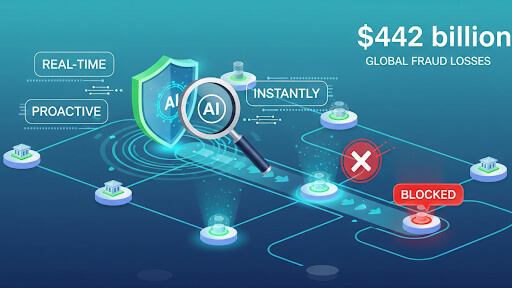
- Fraud Detection and Alerts: Proactively calling customers with real-time fraud alerts and executing immediate account locks or transaction confirmations.
- Loan Servicing: Answering initial loan eligibility questions or assisting with payment schedules and invoice requests. A notable example is Bank of America’s “Erica,” which has handled over a billion user interactions, demonstrating the massive scale that is achievable.
Retail and ecommerce
Voice AI agents are critical in managing the high-volume, transactional nature of the modern retail environment.
- Order Tracking and Management: Providing instant, real-time updates on shipping status, changing delivery addresses, or modifying/canceling recent orders.
- Returns and Refunds: Guiding customers through the returns process, checking eligibility, and automatically issuing return shipping labels via email or SMS.
- Voice Product Recommendations: Acting as a personal shopper, the agent can use past purchase data to offer personalized recommendations (e.g., “Find me an eco-friendly running shoe in size 9 with free shipping”).
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Agents enhance patient experience while strictly maintaining compliance (e.g., HIPAA).
- Appointment Scheduling: Automatically booking, rescheduling, or canceling appointments based on real-time provider availability.
- Prescription Refills: Handling automated prescription refill requests and sending confirmations to pharmacies.
- Information Dissemination: Providing answers to frequently asked questions about billing, insurance coverage, or facility locations.
Travel and Hospitality
Voice AI agents in this sector focus on delivering seamless, personalized, and multilingual support for guests and travelers around the clock.
- Booking Management: Assisting with booking, modifying, or canceling flights, hotel rooms, or rental cars, often integrating with global distribution systems (GDS).
- AI Concierge Services (Hotels): Inside hotel rooms, agents can fulfill immediate guest requests (e.g., “order room service,” “schedule a wake-up call,” “request extra towels”) and provide information about amenities or local attractions.
- Loyalty Program Inquiries: Answering questions about reward points, tier status, and program benefits.
Telecommunications and Utilities
These industries manage vast customer bases and handle high volumes of repetitive, service-related calls concerning bills, service status, and technical issues.
- Billing and Payment Management: Automatically processing bill payments, answering detailed inquiries about charges, and setting up payment plans without a human agent.
- Service Outage and Status Alerts: Providing real-time, automated updates on service interruptions (e.g., internet or power outages) based on the customer’s location and account status.
- Technical Troubleshooting: Guiding customers through initial steps for troubleshooting common issues (e.g., “reset your modem”) and instantly escalating to a human agent only for complex problems.
- Service Activation/Deactivation: Handling requests for new service setup, upgrades, or cancellations, verifying account details through voice biometrics.
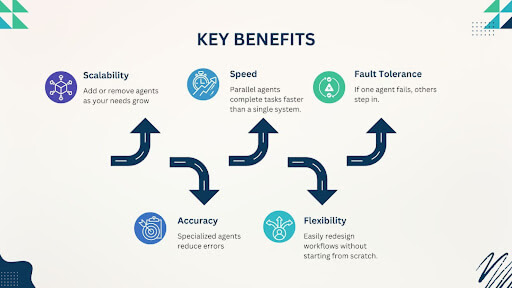
The Advantages of Employing Voice AI Agents
Voice AI agents are transforming business operations and customer interactions. Utilizing natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, these systems provide benefits that enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and reduce operational costs.
1. Unmatched Availability and Speed
- 24/7 Service: Unlike human teams, which are restricted by business hours and time zones, Voice AI agents provide instant, round-the-clock support. This continuous availability ensures that customer inquiries are addressed immediately, regardless of when they occur.
- Rapid Response and Resolution: AI agents can eliminate wait times and instantly handle routine questions. By simultaneously accessing multiple back-end systems (like CRM and knowledge bases), they can provide complete, accurate answers and resolve common issues much faster than traditional methods, significantly improving First Call Resolution (FCR) rates.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Scalability
- Cost Reduction: By automating high-volume, repetitive tasks such as answering FAQs, collecting data, and initial screening, Voice AI agents dramatically lower operational costs, as they can manage thousands of concurrent calls without increasing staff headcount.
- Seamless Scalability: Voice AI systems can instantly scale to manage sudden demand spikes, such as during peak seasons or service outages, ensuring consistent service quality without delays or degradation.
- Increased Human Agent Productivity: By offloading simple, routine inquiries, AI agents free up human staff to concentrate on complex, high-value, or emotionally sensitive issues that require critical thinking, thereby maximizing the overall productivity of the workforce.
3. Superior and Consistent Customer Experience (CX)
- Consistent Quality: AI agents ensure every customer interaction is handled according to set policies and deliver standardized, accurate information. This consistency eliminates the variability that can arise from human factors, such as fatigue or varying training levels.
- Natural and Hands-Free Interaction: Advanced natural language processing (NLP) allows for fluid, human-like conversations, where customers can speak naturally without having to navigate rigid phone menus. This hands-free experience is convenient for users and increases overall customer satisfaction (CSAT).
- Multilingual Support: Voice AI agents can communicate fluently in multiple languages and even understand various dialects and accents. This capability enables businesses to efficiently serve a global customer base and eliminate language barriers without incurring the expense of building large, diverse support teams.
Conclusion
The evolution from the IVR to the intelligent, autonomous Voice AI Agent represents more than just an incremental update; it is the foundation of the Autonomous Enterprise. By leveraging sophisticated technologies like Agentic RAG and emotional AI, these systems redefine customer service by delivering instant, personalized, and highly accurate interactions at an immense scale.
The future of CX is one where AI agents handle the transactional, repeatable aspects of service, ensuring operational efficiency and cost savings, while human employees are elevated to focus on the truly empathetic and high-stakes interactions. For businesses aiming to secure market leadership and foster deep customer loyalty, adopting these best AI voice agents is no longer optional; it is a mandatory step toward achieving world-class customer experience.
FAQs
1) What exactly is a Voice AI Agent?
A Voice AI Agent is an intelligent software system that uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand human speech, process natural language, and respond with a human-like voice in real-time conversations. They are designed to manage complex, multi-step tasks autonomously.
2) How do Voice AI Agents differ from traditional IVR systems?
Traditional IVR systems are rigid and menu-driven. They mainly route calls or play pre-recorded responses. AI Agents are proactive and autonomous. They utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate responses, resolve complex issues, and maintain conversation context.
3) What are the core benefits of implementing a Voice AI Agent?
- 24/7 Availability: Providing instant, round-the-clock service.
- Scalability: Handling virtually unlimited call volumes without a drop in service quality.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By automating routine and repetitive inquiries.
- Improved Customer Experience: Through faster resolution times and consistent, personalized interactions.
4) Can Voice AI Agents handle complex or non-standard requests?
Yes. Modern Voice AI Agents, especially those powered by Generative AI and LLMs, are capable of reasoning. They can break down complex goals into subtasks, integrate with backend systems (such as CRM or inventory), and carry out multi-step actions to resolve requests that go beyond simple FAQs.
How Can [x]cube LABS Help?
At [x]cube LABS, we craft intelligent AI agents that seamlessly integrate with your systems, enhancing efficiency and innovation:
- Intelligent Virtual Assistants: Deploy AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants for 24/7 personalized customer support, streamlining service and reducing call center volume.
- RPA Agents for Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like invoicing and compliance checks, minimizing errors and boosting operational efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics & Decision-Making Agents: Utilize machine learning to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and provide real-time strategic insights.
- Supply Chain & Logistics Multi-Agent Systems: Enhance supply chain efficiency by leveraging autonomous AI agents that manage inventory and dynamically adapt logistics operations.
- Autonomous Cybersecurity Agents: Enhance security by autonomously detecting anomalies, responding to threats, and enforcing policies in real-time.
- Generative AI & Content Creation Agents: Accelerate content production with AI-generated descriptions, visuals, and code, ensuring brand consistency and scalability.
Integrate our Agentic AI solutions to automate tasks, derive actionable insights, and deliver superior customer experiences effortlessly within your existing workflows.
For more information and to schedule a FREE demo, check out all our ready-to-deploy agents here.
 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783