Artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, and the generative AI tech stack is emerging as a powerful tool that can transform industries.
Generative AI utilizes machine learning algorithms and intense learning models to create entirely new data realistic images, compelling text formats, or even original musical pieces.
This technology is making waves across various sectors, from revolutionizing product design in e-commerce to accelerating drug discovery in pharmaceutical research.
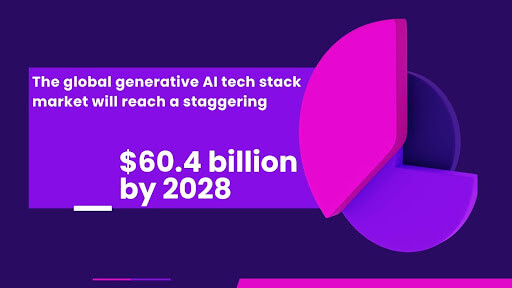
A recent report by Grand View Research predicts the global generative AI tech stack market will reach a staggering $60.4 billion by 2028, underscoring the urgent need to understand and adopt this rapidly growing AI technology.
However, building and scaling robust Generative AI stack systems is complex. It requires a well-defined tech stack, which is crucial to the success of any Generative AI project.
This underlying infrastructure provides developers and data scientists with the tools and resources to design, train, deploy, and continuously improve their Generative AI models.
Understanding and effectively utilizing the Generative AI tech stack is a matter of interest and a crucial step for maximizing Generative AI’s potential and unlocking its transformative capabilities.
This comprehensive guide is designed for developers, data scientists, and AI enthusiasts eager to delve into the world of Generative AI.
We’ll examine the essential elements of the Generative AI technology stack and outline the vital tools and considerations for building and scaling successful Generative AI systems.
Demystifying the Generative AI Tech Stack
Building effective generative AI systems hinges on a robust tech stack, with each component playing a crucial role. Let’s delve into the key elements:
A. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
- High-Quality Data is King: Generative AI models are data-driven, learning from existing information to create new outputs. The caliber and volume of data directly impact the efficacy of the model. A 2022 Stanford study found that the performance of generative models significantly improves with more extensive and diverse datasets.
- Data Collection and Cleaning: Gathering relevant data can involve web scraping, public datasets, or proprietary sources. Data cleaning is essential, as inconsistencies and errors can negatively influence the model’s training. Techniques like normalization, anomaly detection, and filtering are often used.
- Augmentation is Key: Generative AI thrives on diverse data. Techniques like data augmentation (e.g., rotating images, adding noise) can artificially expand datasets and improve model robustness.
- Data Privacy Considerations: With increasingly stringent regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, ensuring data privacy is paramount. Anonymization and differential privacy can protect user information while enabling model training. This has led to a major rise in the importance of Synthetic Data Management as a critical application for addressing privacy compliance and data scarcity. Vector Databases are becoming key components here for efficient data retrieval and context management.
B. Machine Learning Frameworks: Building the Foundation
Machine learning frameworks provide the tools and libraries for designing and training neural networks, the core building blocks of generative AI models. Popular choices include:
- TensorFlow: Developed by Google, it offers a comprehensive suite of tools for building and deploying various AI models, including generative models.
- PyTorch: Known for its ease of use and flexibility, PyTorch is a popular choice for research and rapid prototyping of generative models.
- JAX: A high-performance framework from Google AI, JAX excels at numerical computation and automatic differentiation, making it well-suited for complex generative models.
C. Core Generative AI Models
The generative AI landscape boasts various models, each with its own strengths:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Imagine two neural networks locked in competition. One (generator) creates new data, while the other (discriminator) tries to distinguish accurate data from the generated output. This adversarial process produces highly realistic outputs, making GANs ideal for image and video generation. While overtaken by Diffusion Models for images, GANs still hold significant value in specialized synthetic data generation and certain research areas.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs learn a compressed representation of the data (latent space) and can generate new data points within that space. This allows anomaly detection and data compression, making VAEs valuable in various applications.
- Autoregressive Models: These models generate data one element at a time, taking into account previously generated elements. Transformer-based models, underpinning Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT and Gemini, account for a dominant share of the generative AI market due to their ability to efficiently handle vast amounts of data for text, code, and multimodal tasks.
D. Scalable Infrastructure (Scaling Generative AI Systems)
- The Power of the Cloud: Training generative AI models can be computationally intensive. Scalable cloud infrastructures like Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure provide the resources and flexibility needed to train and deploy these models efficiently. A report by Grand View Research estimates the cloud AI market to reach a staggering $169.8 billion by 2028, demonstrating the rising need for AI solutions based in the cloud.
- The Hardware Layer (The AI Silicon Supercycle): The backbone of this stack is specialized hardware. There is an ongoing “AI Silicon Supercycle” driven by demand for specialized accelerator chips (primarily GPUs from companies like NVIDIA and AMD) engineered to meet the unique computational demands of training and running LLMs and Diffusion Models. This infrastructure race is what enables high-speed, large-scale AI deployment.
E. Evaluation, Monitoring, and the Rise of Agents
- Evaluating for Success: Like any system, generative AI models require careful evaluation. Success metrics vary depending on the task. For example, image generation might involve measuring image fidelity (how realistic the generated image appears). Text generation can be evaluated for coherence and grammatical correctness, while music generation might be assessed based on musicality and adherence to a specific style.
- Continuous Monitoring is Crucial: Once deployed, generative models should be continuously monitored for performance and potential biases. Techniques like A/B testing and human evaluation can help identify areas for improvement. Addressing biases in generative AI models is an ongoing area of research, as ensuring fairness and inclusivity is critical for responsible AI development.
- The Rise of Agentic AI: A significant recent development is the rise of Agentic AI. These are autonomous or semi-autonomous systems built on top of the generative tech stack that can perceive, reason, plan, and take a sequence of actions on their own to achieve a complex goal. This shift from simple content generation to complex, automated workflows represents the next major step in enterprise AI implementation.
By understanding these core components of the generative AI tech stack, you can build and scale your own generative AI tech stack systems, unlocking the power of this transformative technology.
Building Your Generative AI System: A Step-by-Step Guide
The success of any generative AI project is not just a matter of chance; but it hinges on a well-defined roadmap and a robust tech stack.
- Start with Defining the Problem and Desired Outcome: This is the crucial first step in your generative AI tech stack project. It’s about clearly understanding the challenge you want to address. A generative AI tech stack can tackle various tasks, from creating realistic images to composing music. Be specific about the desired output (e.g., high-fidelity product images for e-commerce) and how it will benefit your application.
- Gather and Pre-process Relevant Data: Generative AI models are data-driven, so high-quality data is paramount. The amount and type of data will depend on your specific task. For instance, generating realistic images requires a large dataset of labeled images. Data pre-processing involves cleaning, organizing, and potentially augmenting the data to ensure the model learns effectively. A study by Andrew Ng et al. 2017 found that the data required for training effective generative models has steadily decreased, making them more accessible for projects with smaller datasets.
- Please choose the Appropriate Generative AI Model and Framework: The generative AI tech stack landscape offers various models, each with strengths and weaknesses. Popular choices include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for creating high-fidelity images, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) for data generation and anomaly detection, and Autoregressive models for text generation. When selecting the most suitable model type, consider specific task requirements (e.g., image quality, text coherence). Additionally, choose a machine learning framework like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or JAX that aligns with your development preferences and offers functionalities for building and training the selected model.
- Train and Evaluate the Model: This is where the magic happens! Train your generative AI model on the pre-processed data. The training involves adjusting the model’s parameters to achieve the desired outcome. Continuously evaluate the model’s performance using metrics relevant to your task. Image generation might involve assessing image fidelity and realism. For text generation, metrics like coherence and grammatical correctness are crucial. Based on the evaluation results, refine the model’s architecture, training parameters, or chosen model type.
- Deploy the Model on Scalable Infrastructure: Once you’re satisfied with its performance, it’s time to deploy it for real-world use. Training and using generative AI models can be computationally costly. To ensure your model can handle real-world demands, consider leveraging scalable cloud infrastructure platforms like Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS), or Microsoft Azure.
- The journey doesn’t end with deployment: Continuous monitoring and improvement of generative models is not just a suggestion but a crucial step for maintaining their performance and addressing potential biases. This might involve retraining the model on new data or adjusting its parameters to address potential biases or performance degradation over time. By following these steps and leveraging the power of the generative AI tech stack, you can build and scale your generative AI tech stack system to unlock new possibilities in your field.
Case Studies: Generative AI Applications Across Industries
The generative AI tech stack is rapidly transforming numerous industries beyond healthcare.
Here are some compelling examples that showcase the power of this technology: Revolutionizing E-commerce with Realistic Product Images: A significant challenge for e-commerce platforms is the cost and time associated with professional product photography.
The generative AI application is changing the game. Generative models can analyze existing product images and descriptions to create high-quality, realistic images from various angles and lighting conditions.
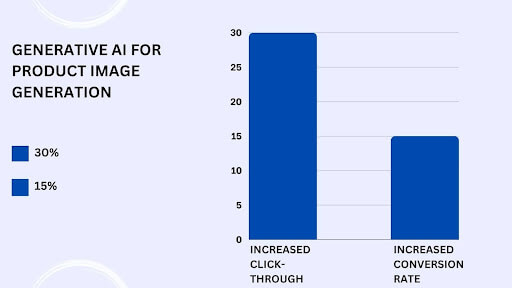
A study found that using generative AI for product image generation increased click-through rates by 30% and conversion rates by 15%, highlighting the significant impact on customer engagement and sales.
Overcoming Data Scarcity with Synthetic Datasets: Training powerful AI models often requires massive amounts of real-world data, which can be costly and labor-intensive to gather.
Generative AI tech stack offers a solution by creating synthetic datasets that mimic accurate data.
For instance, generative models in the self-driving car industry can create realistic traffic scenarios for training autonomous vehicles.
A report by McKinsey & Company estimates that synthetic data generation using generative AI has the potential to unlock $3 trillion in annual value across various industries by 2030.
Democratizing Content Creation with Personalized Tools: The generative AI tech stack is not just a tool for professionals; it empowers individuals to become content creators.
AI-powered writing assistants can help overcome writer’s block by suggesting relevant phrases and generating drafts based on user prompts.
Similarly, generative music platforms allow users to create unique musical compositions by specifying genre, mood, and desired instruments.
A recent study revealed that 60% of marketing professionals already leverage generative AI tools for content creation, demonstrating the growing adoption of this technology for marketing and advertising purposes.
Accelerating Scientific Discovery: The scientific research field also embraces generative AI.
In drug discovery, generative models can design and simulate new molecules with desired properties, potentially leading to faster development of life-saving medications.
A generative AI tech stack is also explored in material science to create novel materials with superior properties for aerospace, energy, and construction applications.
An article highlights how a research team used a generative AI tech stack to discover a new type of solar cell material with a predicted 20% increase in efficiency, showcasing the potential of this technology for scientific breakthroughs.
These illustrations only scratch the surface of generative AI’s enormous potential in various industries.
As the tech stack continues to evolve and generative models become more sophisticated, we can expect even more transformative applications to emerge in the years to come, sparking excitement and anticipation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, building and scaling generative AI tech stack systems requires a robust tech stack encompassing data management, powerful machine learning frameworks, specialized generative models, scalable infrastructure, and continuous monitoring.
By leveraging this comprehensive approach, organizations across diverse fields can unlock generative AI’s immense potential.
The impact of generative AI is already being felt across industries. A recent study by Gartner predicts that by 2025, generative AI will be responsible for creating 10% of all synthetic data used to train AI models, highlighting its role in overcoming data scarcity.
Additionally, a report by IDC estimates that the global generative AI tech stack market will reach a staggering $11.2 billion by 2026, signifying the rapid adoption of this technology.
Advances in generative AI models and the tech stack will further accelerate their transformative potential.
As the tech stack matures, we can expect even more innovative applications in areas like personalized education, climate change mitigation, and autonomous systems. The possibilities are boundless.
This guide’s knowledge and resources strengthen you to join the forefront of this exciting technological revolution.
By understanding the generative AI tech stack and its potential applications, you can explore how to leverage this technology within your field and contribute to shaping a future driven by innovation and progress.
FAQs
1. What’s the core of a generative AI tech stack?
The core comprises a foundation model (such as an LLM), high-performance GPU or TPU infrastructure, and machine learning frameworks like PyTorch. Additionally, a vector database grounds the model in proprietary data, while an orchestration framework (for example, LangChain) handles complex application workflows.
2. What are the key layers of a typical Generative AI tech stack?
A modern stack is often broken down into four core layers:
- Infrastructure (e.g., GPUs, TPUs, Cloud platforms).
- Model (Foundation Models, Fine-Tuned Models, Frameworks like PyTorch).
- Data (Vector Databases for RAG, Data Processing).
- Application/UX (Orchestration Frameworks, APIs, User Interfaces).
3. What is the single biggest technical hurdle when scaling a Generative AI application?
Computational Cost and Latency. Serving large Foundation Models requires massive, expensive GPU resources, and optimizing the inference process to deliver low-latency responses (often using techniques like continuous batching and quantization) is the main scaling bottleneck.
4. What’s the future of generative AI?
The future centers on fully autonomous agents able to execute complex, multi-step tasks independently, and on multi-modal models that interpret and generate text, images, video, and audio. There will also be significant effort toward making models smaller, faster, and more efficient through advances in quantization and optimization.
5. What is the difference between a Foundation Model and a Fine-Tuned Model in the AI technology stack?
A foundation model (such as Gemini or GPT-4) is a large-scale model pretrained on a vast, general-purpose dataset. A fine-tuned model adapts a foundation model by further training it on a smaller, domain-specific dataset (e.g., using LoRA) to specialize for a focused enterprise task.
How Can [x]cube LABS Help?
At [x]cube LABS, we craft intelligent AI agents that seamlessly integrate with your systems, enhancing efficiency and innovation:
- Intelligent Virtual Assistants: Deploy AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants for 24/7 personalized customer support, streamlining service and reducing call center volume.
- RPA Agents for Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like invoicing and compliance checks, minimizing errors and boosting operational efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics & Decision-Making Agents: Utilize machine learning to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and provide real-time strategic insights.
- Supply Chain & Logistics Multi-Agent Systems: Enhance supply chain efficiency by leveraging autonomous agents that manage inventory and dynamically adapt logistics operations.
- Autonomous Cybersecurity Agents: Enhance security by autonomously detecting anomalies, responding to threats, and enforcing policies in real-time.
- Generative AI & Content Creation Agents: Accelerate content production with AI-generated descriptions, visuals, and code, ensuring brand consistency and scalability.
Integrate our Agentic AI solutions to automate tasks, derive actionable insights, and deliver superior customer experiences effortlessly within your existing workflows.
For more information and to schedule a FREE demo, check out all our ready-to-deploy agents here.
 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783