 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783 
The emergence of artificial intelligence agents represents a fundamental paradigm shift in business technology, with significant potential for AI agents business applications. For years, AI has been a reactive assistant, enhancing individual productivity but often failing to transform core business processes. This is the “gen AI paradox”: real value is spread thinly, improving single tasks without revolutionizing the enterprise.
The true game-changer is the move from reactive tools to proactive collaborators. This is the domain of AI agents business applications. Unlike their predecessors, AI agents are designed for autonomy. They can automate entire complex business processes by combining planning, memory, and system integration. This transition marks the dawn of the “proactive enterprise,” where intelligent systems anticipate needs, identify opportunities, and execute multi-step actions to achieve strategic goals.
Business leaders are no longer asking what AI can generate, but what it can do. This demand for tangible, process-level ROI is driving the adoption of AI agents in business applications. Businesses now seek robust, autonomous solutions that can coordinate workflows and make decisions without constant human intervention, solving higher-order problems and driving meaningful growth.
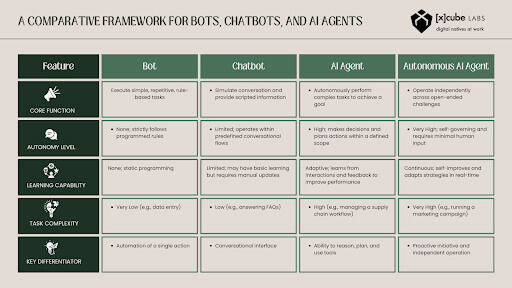
To grasp the strategic importance of AI agents, it’s crucial to distinguish them from simpler technologies, such as bots and chatbots. Bots are simple programs that follow predefined rules, while chatbots simulate conversation within a limited script. They retrieve information but cannot reason or act upon it.
AI agents are a quantum leap forward. An agent is a software program that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes autonomous actions to achieve specific goals. Even more advanced are autonomous AI agents business applications, which operate with a high degree of independence, learning and adapting as they tackle open-ended challenges.
The core difference is the shift from a static “knowledge base” to a dynamic “cognitive architecture.” An AI agent can perceive, reason, plan, and act upon a changing world, making it a truly transformative tool.
The adoption of AI agents in business applications creates a compounding “multiplier effect,” driving tangible outcomes across the organization.
Agents create a leaner, more efficient organization by automating complex workflows, not just simple tasks. This increases productivity by freeing employees for strategic work and reduces costs by minimizing manual labor and human error. Agents execute functions with high precision and consistency, often self-correcting to maintain accuracy.

Beyond efficiency, agents provide a potent strategic edge. They analyze vast datasets to empower data-driven decision-making, turning information into a source of strategic value. An agent-based workforce is also highly scalable, allowing companies to expand or contract operations in real-time to meet demand without a proportional increase in overhead. By connecting disparate systems, agents can break down departmental silos, creating a more integrated and responsive organization.
The most profound impact of AI agents is their ability to drive top-line growth. Agents can deliver hyper-personalized customer experiences, which have been shown to increase customer satisfaction by up to 40%. They can also amplify existing revenue by identifying upselling opportunities in real time. Most importantly, their autonomy enables entirely new business models, such as pay-per-use or performance-based subscriptions for industrial equipment, shifting the focus from selling products to selling guaranteed outcomes.
The benefits of AI agents are being proven across every industry. These AI agent business application examples demonstrate their ability to drive efficiency and growth by automating complex workflows that span multiple business functions.
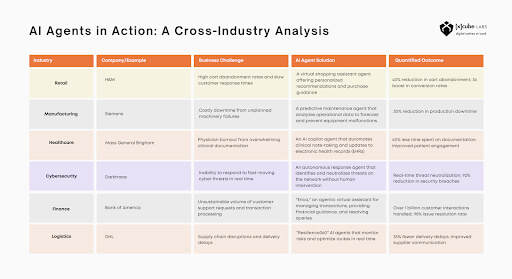
In finance, AI agents are utilized in business applications to conduct risk audits and automate accounting tasks. Bank of America’s “Erica” has handled over a billion customer interactions, resolving 98% of issues autonomously. In retail, H&M’s virtual assistant has tripled conversions, while in manufacturing, Siemens utilizes agents for predictive maintenance, resulting in a 30% reduction in downtime. The healthcare sector is using AI agents in business applications to alleviate administrative burdens, freeing physicians to save up to 60% of their time on paperwork.
Looking toward AI agents business applications 2025, the landscape is set to evolve dramatically, shifting from single agents to interconnected systems.
The next frontier is multi-agent systems, also known as “swarms,” where teams of specialized agents collaborate to solve complex challenges, such as simulating a new product launch. This will also redefine human roles, giving rise to the “agent boss,” an employee who manages a team of AI agents to amplify their own impact. This new model will require a massive focus on upskilling.
As agents become more autonomous, governance and trust will become Top-Level priorities for CEOs. The fear of an agent making a critical error is a real barrier to adoption, and overcoming this “trust gap” will be crucial. The companies that lead will be those that invest as heavily in change management and transparent governance as they do in the technology itself.
Successfully integrating AI agents is a strategic transformation that requires a clear blueprint.
Step 1: Define Goals and Identify High-Impact Opportunities Begin with a clear business objective. Map key processes to identify pain points where agents can deliver high impact with manageable complexity, securing early wins to build momentum.
Step 2: Explore Solutions and Select the Right Agent Architecture. AI agents are not one-size-fits-all. Select the right agent architecture, whether a single agent or a multi-agent system, that best fits the specific business problem you are trying to solve.
Step 3: Pilot, Build Trust, and Scale with a Modular Approach Use a phased approach centered on pilot projects. Begin with a focused use case to demonstrate value and establish trust among stakeholders. A modular architecture makes it easier to test, refine, and scale over time.
Step 4: Manage the Change and Foster a Collaborative Culture The most significant challenge is often cultural. Redesign business processes to leverage AI’s full capabilities and invest heavily in upskilling your workforce to collaborate with and manage AI agents.
Step 5: Evaluate Outcomes, Iterate, and Optimize Establish clear KPIs to track the impact of agents on business goals. Use this data-driven feedback loop to continuously refine and optimize your agents and strategy, ensuring the investment delivers compounding returns.
The business landscape is at the precipice of a transformation driven by the shift from task automation to genuine process autonomy, which is a present-day reality. This shift delivers quantifiable value by enhancing productivity, personalizing customer experiences, and creating new revenue streams.
The adoption of is no longer an option; it is a necessity for growth. The journey requires a strategic commitment to reimagining processes, fostering a culture of human-agent collaboration, and building the governance frameworks necessary to maintain trust. The organizations that successfully navigate this agentic shift will not only be more efficient; they will also be more intelligent, agile, and capable of delivering value in the future economy.
1. What is the difference between AI agents and chatbots in business applications?
Chatbots follow predefined scripts. In contrast, AI agents business applications can reason, learn, and autonomously perform complex tasks. Agents take action, while chatbots just provide information.
2. Can you provide examples of AI agents in business applications?
Key AI agents business applications examples include Bank of America’s “Erica” for customer service, Siemens’ system for predictive maintenance, and Darktrace’s agent for real-time cybersecurity threat neutralization.
3. How do autonomous AI agents drive business growth?
Autonomous AI agents business applications boost growth by increasing efficiency and reducing costs. They also enable data-driven decisions and create new revenue by personalizing customer experiences and facilitating new service models.
4. What makes an AI agent “autonomous”?
An autonomous AI agent operates with a higher degree of independence. It can learn and make its own decisions to solve complex problems with minimal human input, a key feature of advanced AI agents in business applications.
5. What is the outlook for AI agents in business applications for 2025?
For AI agents business applications in 2025, expect increased adoption and sophistication. Key trends include the rise of collaborative multi-agent systems (“swarms”) and a growing focus on AI governance as agents take on increasingly critical business tasks.
At [x]cube LABS, we craft intelligent AI agents that seamlessly integrate with your systems, enhancing efficiency and innovation:
Integrate our Agentic AI solutions to automate tasks, derive actionable insights, and deliver superior customer experiences effortlessly within your existing workflows.
For more information and to schedule a FREE demo, check out all our ready-to-deploy agents here.